javafx?
由Sun公司发布于2008年12月05日,多用于编写窗体程序。界面由xml文件设计完成,在java源码中使用注解获取xml文件定义的控件以及定义事件。相较于java swing提供了更多控件并且更易于使用。
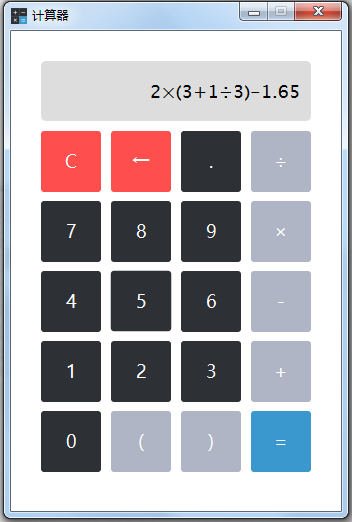
运行效果
实现原理
整体思路
这是一个经典的用栈求解表达式的问题。这里将操作数和运算符统称为运算单元,并且会在表达式的两端分别添加一个#,表示表达式的开始与结束。首先建立操作数以及运算符两个栈,按照表达式的顺序,取一个运算单元,如果取到的是一个操作数,将其入栈并取下一个运算单元;如果取到的是一个运算符,将其与运算符栈的栈顶运算符的优先级进行比较,若栈顶运算符的优先级较低,将新运算符入栈并取下一个运算单元,若优先级相等,将栈顶运算符退栈并取下一个运算单元,若栈顶运算符的优先级较高,从操作数栈退栈两个数分别作为操作数2和操作数1,从运算符栈退栈一个运算符,对两个操作数作该运算,并入栈操作数栈。最终的运算结果就是操作数栈的栈顶元素。
表达式优先级表如下所示。叹号表示绝对不可能出现的对比,出现则可以认为表达式有误,倒数第三行和最后一行的叹号说明发生了小括号不匹配,而倒数第二行则是因为右括号绝对不可能入栈。
| op1/op2 | + | - | × | ÷ | ( | ) | # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | > | > | < | < | < | > | > |
| - | > | > | < | < | < | > | > |
| × | > | > | > | > | < | > | > |
| ÷ | > | > | > | > | < | > | > |
| ( | < | < | < | < | < | = | ! |
| ) | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! |
| # | < | < | < | < | < | ! | = |
具体实现
1.定义Unit类表示运算单元
运算单元,表示一个操作数或者一个运算符。
1 |
|
2.表达式转为运算单元的列表
之所以进行这一步,是因为操作数占得字符长度一般大于1,而且需要考虑可能存在的小数点以及正负号。在转运算单元时还考虑到了几种特殊的操作数,由非0数除以0得到的无穷,以及未定义结果NaN(比如0/0,正无穷加负无穷,结果均为NaN)。如果判断出表达式错误将抛出自定义异常。
1 | private static List<Unit> parseUnits(String s) throws ExpressionIllegalException{ |
3.计算
运算符优先级的比较。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21/**
* 根据优先级矩阵返回两个运算符优先级比较的结果
* !表示不可能出现比较这两个运算符的情形,可认为输入有误
* 乘法接受*或×两种符号
* 除法接受/或÷两种符号
*/
public static char compareOperator(char op1, char op2){
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
map.put('+', 0);
map.put('-', 1);
map.put('×', 2);
map.put('*', 2);
map.put('÷', 3);
map.put('/', 3);
map.put('(', 4);
map.put(')', 5);
map.put('#', 6);
String[] compare = new String[]{">><<<>>", ">><<<>>", ">>>><>>", ">>>><>>", "<<<<<=!", "!!!!!!!", "<<<<<!="};
return compare[map.get(op1)].charAt(map.get(op2));
}
表达式的求值。若判断出表达式错误统一抛出自定义异常。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40private static double _calculate(String s) throws ExpressionIllegalException{
List<Unit> units = new ArrayList<Unit>();
units.add(new Unit('#'));
units.addAll(parseUnits(s));
units.add(new Unit('#'));
Stack<Unit> operators = new Stack<Unit>();
Stack<Unit> operands = new Stack<Unit>();
int index = 0;
while(index < units.size() || operators.size() != 0){
Unit unit = units.get(index);
if(unit.getUnitType() == Unit.UnitType.OPERAND){
operands.push(unit);
index += 1;
}else if(unit.getUnitType() == Unit.UnitType.OPERATOR){
if(operators.empty() || compareOperator(operators.peek().getOp(), unit.getOp()) == '<'){
operators.push(unit);
index += 1;
}else if(compareOperator(operators.peek().getOp(), unit.getOp()) == '='){
Unit tmp = operators.pop();
index += 1;
}else if(compareOperator(operators.peek().getOp(), unit.getOp()) == '>'){
if(operands.size() < 2){
throw new ExpressionIllegalException();
}
Unit operand2 = operands.pop();
Unit operand1 = operands.pop();
Unit operator = operators.pop();
Unit res = operator.operate(operand1, operand2);
operands.push(res);
}else{
throw new ExpressionIllegalException();
}
}
}
double res = operands.peek().getVal();
return res;
}
4.格式化输出
之所以特地判断是否NaN是因为后面的函数对于NaN的结果是一个奇怪的字符,而对于正负无穷可以正确的输出。1
2
3
4
5public static String calculate(String s) throws ExpressionIllegalException{
double res = _calculate(s);
return Double.isNaN(res)?"NaN":new DecimalFormat("#.##############").format(res);
}
github
完整的项目已经开源到github上,项目由Intellij IDEA创建。
github项目主页: Calculator